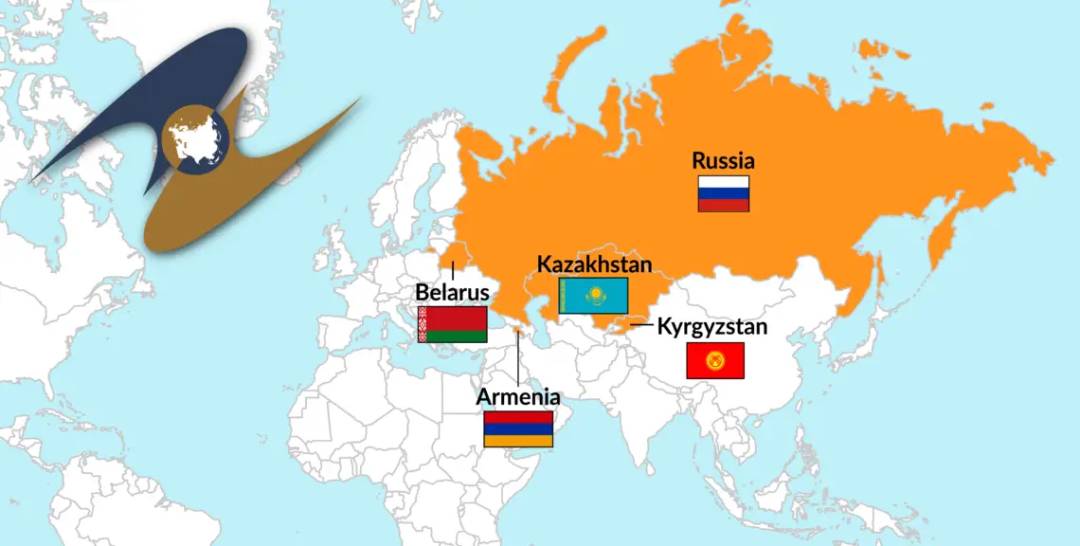
The Eurasian Economic Union is actively expanding its trade territory: it is exploring the establishment of a free trade zone with a number of countries.
Against the backdrop of the evolving global economic landscape, interregional economic cooperation is increasingly becoming a key driver of economic development. Tajikistan's Avesta news agency reported from Dushanbe on August 18 that Russian Minister of Industry and Trade Anton Alikhanov recently disclosed important information that the Eurasian Economic Union is actively planning to set up free trade zones with the United Arab Emirates, Indonesia and Egypt. Currently, the FTA between the Union and these countries is at the stage of active consultations.
Source: Images from the Internet, if there is any infringement, please contact the removal of
On the economic level, there is a large potential for interaction between the BRICS and the Eurasian Economic Union. The BRICS countries, consisting of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, have economies that account for nearly a quarter of the world's GDP and have a significant presence in international trade. The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) is an economic integration organization composed of Russia, Kazakhstan, Belarus, Armenia and Kyrgyzstan, which also has a certain economic influence in the region. On the one hand, the Eurasian Economic Union has rich energy resources, such as Russian oil, natural gas, etc., which is very attractive to the BRICS countries, especially Brazil, China and India, which have a greater demand for energy. Cooperation between the two sides in the field of energy can realize the optimal allocation of resources, such as signing long-term energy supply contracts and jointly carrying out energy development projects, which will bring stable economic returns for both sides. On the other hand, Brazil, India and China among the BRICS countries are large manufacturing countries with advanced technology and rich production experience, which can cooperate with the Eurasian Economic Union countries in the field of manufacturing. For example, they can help Eurasian Economic Union countries to upgrade their manufacturing industries, jointly develop new products and markets, and realize industrial upgrading and transformation.
In the field of trade, the interaction between BRICS countries and the Eurasian Economic Union also has broad prospects. BRICS countries have huge markets and consumer groups, and there is a huge demand for goods and services from Eurasian Economic Union countries. At the same time, the Eurasian Economic Union countries can also provide the BRICS countries with some special products, such as Kazakhstan's agricultural products and Russia's military products, etc. The two sides can promote the growth of trade by lowering trade barriers, strengthening trade facilitation and other measures. In addition, the two sides can jointly promote the signing of regional trade agreements and establish free trade zones to further strengthen trade cooperation. For example, the Russian Minister of Industry and Trade's idea of establishing a common payment system between the Eurasian Economic Union and the BRICS countries, if realized, will greatly reduce trade costs, improve trade efficiency and provide strong support for trade cooperation between the two sides.
From the geopolitical level, the interaction between BRICS and the Eurasian Economic Union is also of great significance. The Eurasian Economic Union is located in the center of the Eurasian continent and is an important bridge connecting Europe and Asia. Cooperation between the BRICS and the Eurasian Economic Union can strengthen economic ties in Eurasia and promote regional stability and development. For Russia, cooperation with the BRICS can mitigate the impact of Western sanctions on its economy and enhance its status and influence on the international stage. For other BRICS countries, cooperation with the Eurasian Economic Union can expand their markets and resources in Eurasia and enhance their voice in regional affairs. At the same time, the cooperation between the two sides can also provide an example of cooperation for other countries and regions and promote the reform and improvement of the global economic governance system.
However, the interaction between BRICS and the Eurasian Economic Union also faces some challenges. First, there are certain differences between the two sides in terms of political systems, levels of economic development and cultural traditions, which may affect the process of cooperation. For example, the two sides may have different views and needs in terms of the formulation of trade rules and standards for market access, which require adequate communication and consultation. Secondly, geopolitical factors may also have an impact on the cooperation between the two sides. The Eurasian Economic Union countries have complicated relations with some Western countries, while some of the BRICS countries also face pressure and challenges from Western countries, which may lead to interference from external factors in the process of cooperation between the two sides. Finally, the two sides need to further strengthen the construction of cooperation mechanisms. At present, both BRICS and the Eurasian Economic Union have their own cooperation mechanisms and platforms, but the interaction between the two sides is not close enough, and there is a need to establish a more effective cooperation mechanism, strengthen information exchange and project docking, and promote the in-depth development of cooperation.
Alikhanov emphasized that FTAs are the most crucial and efficient mechanism in developing the Eurasian Economic Union's partnerships with the outside world. This view highlights the great potential of free trade zones in promoting economic integration, expanding the scale of trade and strengthening regional cooperation. Through the establishment of free trade zones, participating parties can realize mutual benefits in a variety of areas, including trade in goods, trade in services and investment.
In terms of the prospects for cooperation with the UAE, as an important economy in the Middle East, the UAE has a well-developed trade, financial and logistics system. After the establishment of a free trade zone with the Eurasian Economic Union, the two sides are expected to develop in-depth cooperation in the fields of energy, trade and infrastructure construction. For example, in the energy sector, the two sides can further optimize the allocation of energy resources and trade; in trade, the flow of commodities will be smoother, providing more opportunities for enterprises on both sides to develop markets.
As an economic power in Southeast Asia, Indonesia's rich natural resources and huge consumer market have a strong attraction to the Eurasian Economic Union. After the establishment of the free trade zone, the industrial products of the Eurasian Economic Union can enter the Indonesian market more conveniently, and at the same time, Indonesia's agricultural products and minerals can also be exported to the Eurasian Economic Union countries better. This will not only help optimize the trade structure between the two sides, but also drive the development and upgrading of related industries.
As an important economy and trade hub in Africa, the establishment of a free trade zone with the Eurasian Economic Union will bring many benefits to both sides. In the field of agriculture, Egypt's high-quality agricultural products can be in the Eurasian Economic Union market to get a broader sales channels; in the manufacturing sector, the two sides can carry out cooperation in the textile, machinery manufacturing and other areas to achieve industrial complementarity.
In addition, Alikhanov also proposed to consider the possibility of interaction between BRICS countries and the Eurasian Economic Union. This idea opens up new ideas for regional economic cooperation. The BRICS countries have huge economies and rich resources, and interaction with the Eurasian Economic Union can integrate resources, promote trade and investment flows and promote synergistic development of the regional economy on a wider scale.
This series of explorations and consultations shows that the Eurasian Economic Union is moving forward on the road of actively expanding foreign economic cooperation, and is striving to build a more open, diversified and stable economic cooperation network through the establishment of free-trade zones with countries in different regions and of different economic sizes. This will not only have far-reaching significance for the economic development of the participating parties, but will also have a positive impact on the global economic landscape.
-------- END --------